| |
Acupuncture Modalities |
| |
 |
|
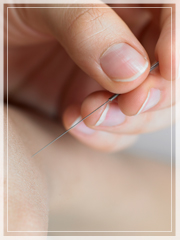
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is the most popular form of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) treatment modalities. Acupuncture involves the insertion of sterilized, single-use, very thin stainless steel needles into specific points on the body known as acupuncture points. The acupuncture points are located on the meridians, where Qi (the vital energy of the body) flows through to provide the body with strength and nourishment. Among over 400 acupuncture points, different acupuncture points are chosen in accordance with patient's individual constitution and presenting signs and symptoms.
The procedure is not painful, although it is common to feel an ache, tightness, or a sensation of heaviness upon the initial insertion.
|
| |
| |
 |
|
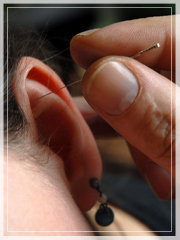
Ear Acupuncture
Ear (auricular) acupuncture is based on the idea that the ear is a micro-system with the entire body represented on the outer portion of the ear. Ailments of the entire body are assumed to be treatable by stimulation of the surface of the ear exclusively.
Auricular acupuncture may be used in conjunction with body acupuncture or as a primary mode of treatment. As a primary therapy, studies have proved that auricular acupuncture is very useful in treating behavioral health, including addictions, mental health, and emotional trauma.
For more information, click here or visit National Acupuncture Detoxification Association (NADA).
|
| |
| |
 |
|
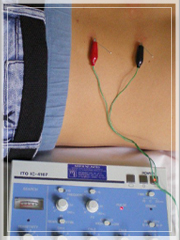
Electro Acupuncture
Electro acupuncture is a form of acupuncture; as with traditional acupuncture, needles are inserted on specific points along the body, then attached to a device that generates continuous electric pulses using small clips. These devices are used to adjust the frequency and intensity of the impulse being delivered, depending on the condition being treated. Electro stimulation enhances the effect of the acupuncture needles and is especially good for treating muscular pain.
|
| |
Adjunctive Modalities |
| |
 |
|
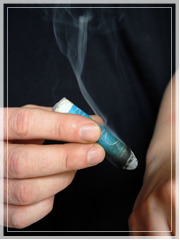
Moxibustion (Moxa)
Moxibustion is the ancient method of burning moxa, a dried herb derived from Chinese mugwort (Artemisia Argyi Folium) leaves, on or near the skin to facilitate healing. In direct moxibustion, a small amount of cone-shaped moxa is placed on top of an acupuncture point and burned. This technique is used less frequently because of the risk of burning the skin. In non-scarring or indirect moxibustion, a smoldering moxa stick (which looks like an oversized cigar) is held over acupuncture points, often above the acupuncture needles. The glowing end of the moxa stick is held about an inch or two above the surface of the skin until the area reddens and becomes suffused with warmth.
Moxibustion is effective in increasing blood flow to areas of injury and warm areas where cold accumulates. This treatment may be used as an adjunct to acupuncture treatment when appropriate, and is used to treat a variety of ailments, including muscle aches and pains, menstrual cramps, and breech pregnancy.
|
| |
| |
 |
|
Cupping
Cupping is one of the oldest Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) treatment modality. It involves the use of glass or plastic cups to create a vacuum seal on the skin. This technique is used to increase circulation to the underlying tissues, disperse swellings, draw toxins out of the tissues, release muscle tension, reduce fever, and activate the lymphatic system.
In dry cupping, the acupuncturist will simply place the suction cups on the skin. In wet cupping, the practitioner will make a small incision on the skin and then apply the suction cup to draw out small amounts of blood.
Cupping can often leave bruise-like marks that may last for a few days after the treatment.
|
| |
| |
 |
|
Gua Sha
Gua Sha is an East-Asian healing technique that involves scraping (Gua) across the skin with an instrument to bring up raised, red marks (Sha).
Gua Sha improves Qi and Blood circulation, opens the skin pores to release the exterior mimicking sweating, and moves fluids containing metabolic waste that has been congested the surface tissues and muscles. Therefore, Gua Sha is often used for pain, aching, tenderness and/or tightness of the muscles associated with acute or chronic disorders. Gua Sha is also used to treat and prevent the common cold, flu, bronchitis, and asthma.
The skin is stroked until Sha is completely raised. The color of Sha has both diagnostic and prognostic value. The darker Sha, the deeper and older Blood Stasis: the skin will only turn pink and Sha will not be formed if there is no Blood Stasis; if Blood Stasis is recent and superficial, Sha is fresh red; if the blood stasis is deeper and chronic, the color of Sha will be dark red, purple, or even black. The discoloration of the skin from Sha should fade in a few days after the therapy.
|
| |
| |
 |
|
Tui Na
Tui Na is a hands-on bodywork technique, which involves brushing, kneading, rolling / pressing and rubbing the areas between each of the joints. Tui Na aims to release tension, increase blood flow, stimulate the release of toxins and encourage muscle repair in the affected area.It is often used to treat musculoskeletal conditions and stress-related disorders of the digestive, respiratory, and reproductive systems.
|
|
|












